Welcome to VLP: Visual Language Perception
A platform for evaluating and comparing visual language models










Visual Language Perception (VLP) serves as a standardized platform for evaluating and comparing visual language models across tasks such as image captioning, visual question answering, and multimodal retrieval. While benchmarks exist for individual tasks, there remains a lack of unified evaluation protocols to assess model robustness in real-world scenarios where vision and language interact dynamically. Current approaches often rely on fragmented datasets with inconsistent metrics, making fair comparisons challenging.
Through VLP, our goal is to establish a comprehensive framework to quantify multimodal understanding and achieve meaningful progress in visual language.
What do we provide?
We have created a platform for fair evaluation of visual language task algorithms. On this platform, we offer:
- A large number of datasets, some of which are already in use, as well as some new challenging sequences!
- A universal evaluation tool that provides multiple metrics ranging from recall, accuracy, ACE, AOR, and more.
- A simple method for comparing the performance of state-of-the-art visual language methods.
We rely on the spirit of crowdsourcing and encourage researchers to submit their test data to our benchmark tests, so that the quality of visual language task algorithms can continue to improve and cope with more challenging scenarios.
News
- February 27, 2025: Wei H, Yang Y, Sun S*, et al. Mono3DVLT: Monocular-Video-Based 3D Visual Language Tracking[C]. CVPR2025.
- February 27, 2025: Guo K, Huang Y, Sun S*, et al. Beyond Human Perception: Understanding Multi-Object World from Monocular View[C]. CVPR2025.
License
The datasets provided on this page are published under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License. This means that you must attribute the work in the manner specified by the authors, you may not use this work for commercial purposes and if you alter, transform, or build upon this work, you may distribute the resulting work only under the same license.
Active Tasks
VLSOT
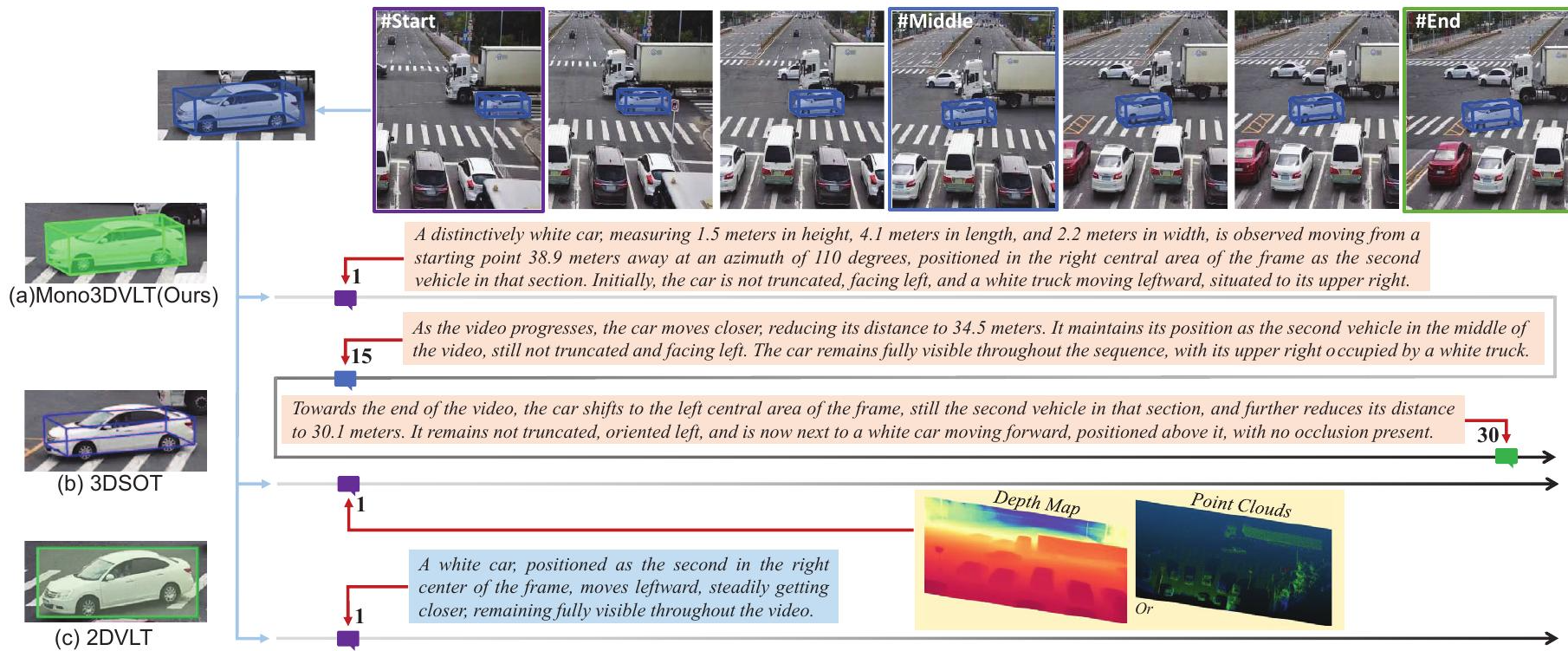
Monocular-Video-Based 3D Visual Language Tracking
- Visual-Language Tracking (VLT) is an emerging paradigm that bridges the human-machine performance gap by integrating visual and linguistic cues, extending single-object tracking to text-driven video comprehension.
- However, existing VLT research remains confined to 2D spatial domains, lacking the capability for 3D tracking in monocular video—a task traditionally reliant on expensive sensors (e.g., point clouds, depth measurements, radar) without corresponding language descriptions for their outputs.
- The code are publicly available (https://github.com/astudyber/Mono3DVLT), advancing low-cost monocular 3D tracking with language grounding.
VLMOD
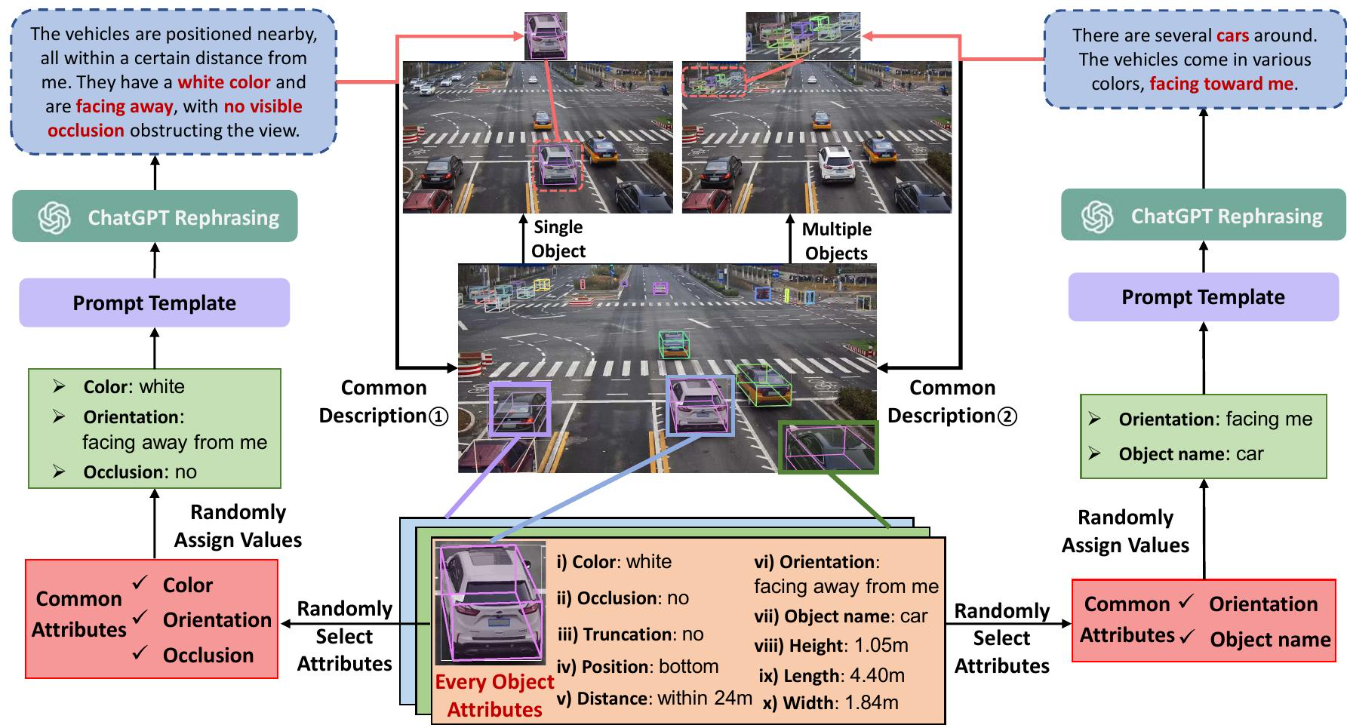
Understanding Multi-Object World from Monocular View
- Language and binocular vision play a crucial role in human understanding of the world. Advancements in artificial intelligence have also made it possible for machines to develop 3D perception capabilities essential for high-level scene understanding.
- However, only monocular cameras are often available in practice due to cost and space constraints. Enabling machines to achieve accurate 3D understanding from a monocular view is practical but presents significant challenges. We introduce MonoMulti-3DVG, a novel task aimed at achieving multi-object 3D Visual Grounding (3DVG) based on monocular RGB images, allowing machines to better understand and interact with the 3D world.
- Our code are available at https://github.com/astudyber/MonoMulti-3DVG
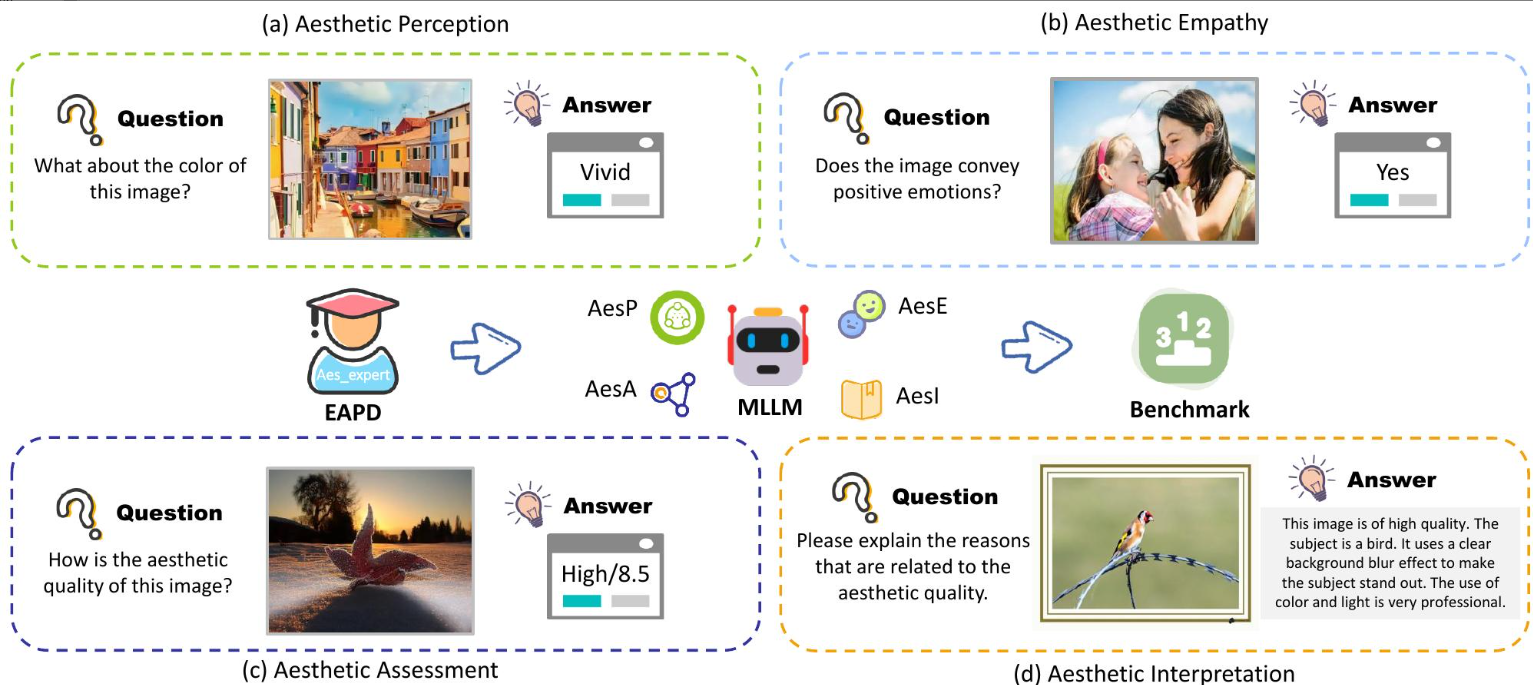
AesBench
Multimodal Large Language Models on Image Aesthetics Perception
- With the rapid development of multimodal large language models (MLLMs), they have shown great potential in human-computer interaction and daily collaboration.
- However, in the important field of aesthetic perception of images, the ability of MLLMs is still unclear, and this ability is crucial for practical applications such as art design and image generation. We hope to inspire further exploration of the aesthetic potential of MLLMs images in academia and industry through AesBench, and make relevant source data public to promote further development in this field.
- Our code are available at https://github.com/yipoh/AesBench
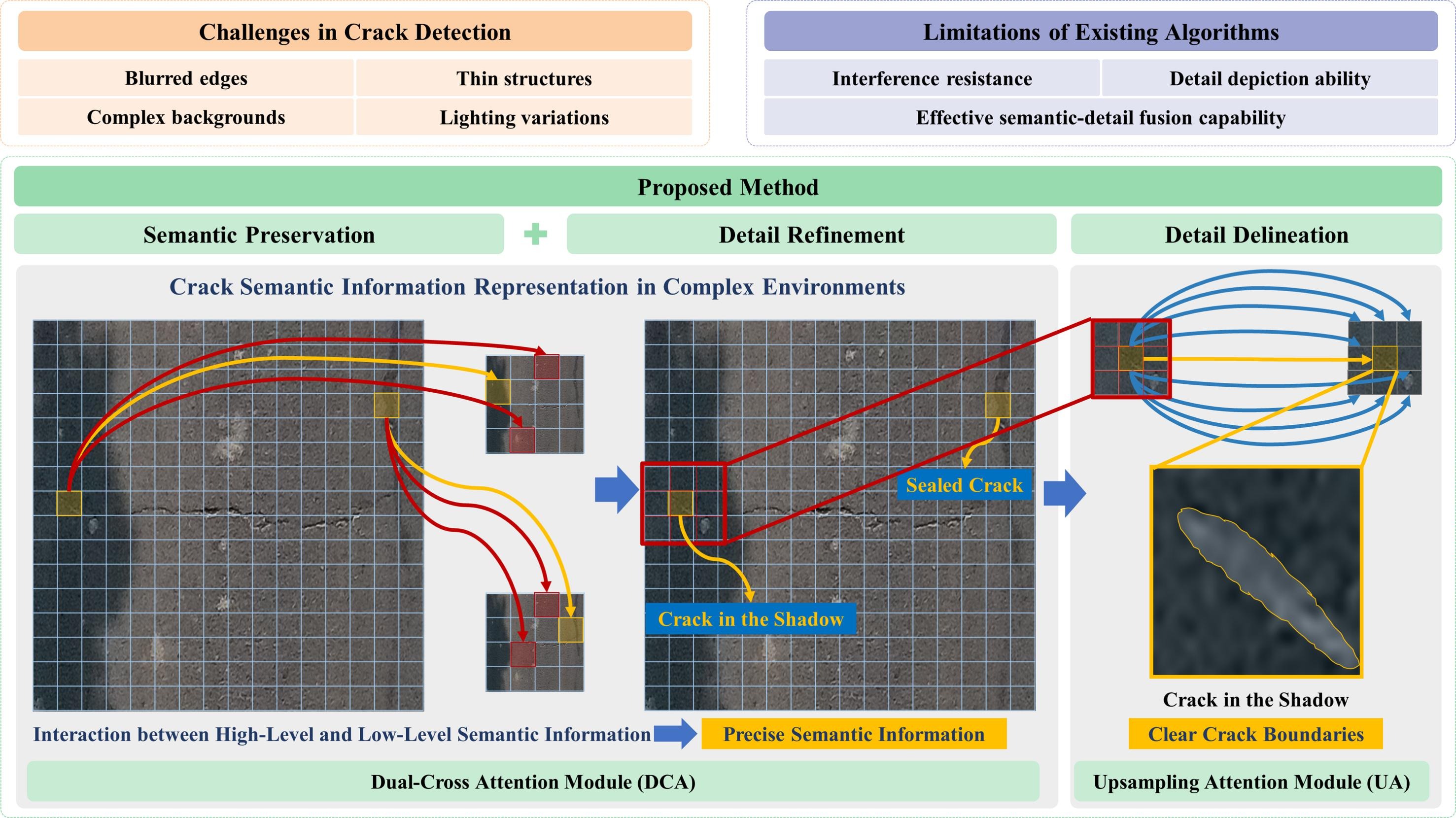
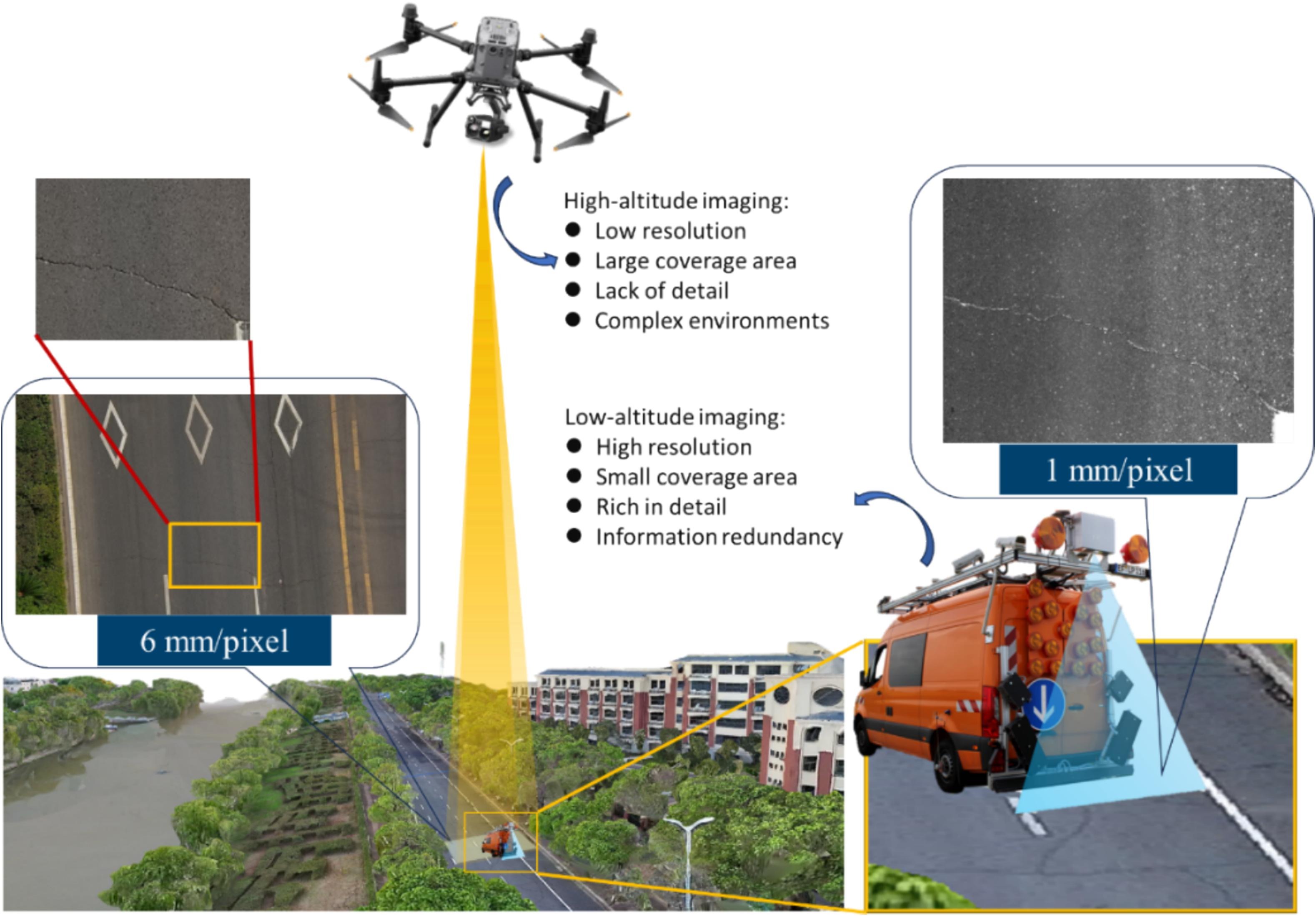
UAV-Crack
UAV-based pavement crack segmentation
- Acquiring pavement distress images with UAVs faces unique challenges compared to ground-based methods due to differences in camera setups, flight parameters, and lighting conditions. These factors cause domain shifts that reduce the generalizability of segmentation models.
- A dedicated dataset, UAV-CrackX, was created with 1500 pixel-wise annotated UAV images to support model development.The dataset includes three subsets—UAV-CrackX4, X8, and X16—with 500 images each at 4×, 8×, and 16× zoom levels.
- Original high-resolution images (2688 × 1512) were split into 16 patches (672 × 378 pixels) for efficient processing. Reference baseline model: https://github.com/open-mmlab/mmsegmentation/tree/main